One of the most important aspects of cost of conversion is manufacturing overhead, which refers to the indirect costs of producing a product or service. To assign manufacturing overhead costs to the products or services, managers need to use allocation bases and rates. In this section, we will explain what allocation bases and rates are, how to choose them, and how to calculate them.
Calculate Your Shipping Costs Now

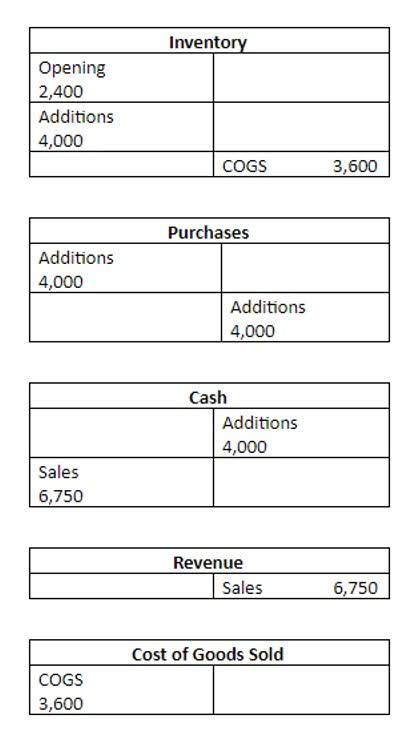
Calculating manufacturing overhead often involves allocating these costs based on machine hours, labor hours, or other relevant factors. How do companies keep track of their expenses, production, sales, and efficiency? Companies largely depend on different metrics to monitor these essential parameters. One such unit is called the ‘conversion costs’ and it refers to the expenses incurred in turning raw materials into inventory that is sellable. In this section, we will delve into the concept of Conversion Cost Variance and explore how it can be measured and analyzed. Conversion costs refer to the expenses incurred during the transformation of raw materials into finished goods.
Experience Simplified Calculations with Sourcetable

Remember, these best practices and examples serve as a starting point for understanding cost of conversion analysis. Each business may have unique considerations and requirements, so it’s important to tailor the analysis to specific circumstances. A company, ABC Co., that manufactures furniture, wants to calculate the conversion cost for the production of a single chair. The company pays $5 for wood that is used conversion cost formula in the production of a chair. The company pays a further $3 for paint and other small materials for a chair. When costs are classified by element, they are classified by whether these costs are related to material, labor or other expenses.
What are Conversion Costs?
Conversion cost is the cost the company spends on unusual expenses and direct labour when turning raw materials into finished products. This costing formula is used in cost accounting by those running manufacturing businesses or any company producing goods. It is used to derive the value of ending inventory and show it https://www.bookstime.com/ in the balance sheet. Some of the same expenses are included in both prime costs and conversion costs. Prime costs and conversion costs, for example, will both include direct labor costs in their estimates.

Mechanics of Applying Conversion Costs
In this blog, we have discussed the concept of cost of conversion, which is the sum of direct labor and manufacturing overhead costs incurred to convert raw materials into finished goods. We Bookkeeping for Startups have also explained how to calculate the cost of conversion using a simple formula and how to allocate it to the units produced using different methods. We have also explored the factors that affect the cost of conversion and how to optimize it to improve the profitability and efficiency of a manufacturing business. In this section, we will summarize the key takeaways and recommendations from our discussion and provide some practical tips for applying them in your own business. The cost of conversion refers to the expenses incurred during the manufacturing process to transform raw materials into finished goods. It includes direct labor costs, factory overhead costs, and other related expenses.
- This is because they are both required to complete the production of that specific item.
- Second, it provides a way to compare the effectiveness of different marketing channels.
- One such unit is called the ‘conversion costs’ and it refers to the expenses incurred in turning raw materials into inventory that is sellable.
- This calculation can be done during any marketing campaign and helps gauge its effectiveness and determine how much your business has made or lost.