
In the short run, firms can temporarily cease operations while still maintaining their productive capacity (by continuing to pay fixed costs). In the long run, if market conditions don’t improve, firms would exit the industry completely rather than merely shutting down production. This amount of revenue is calculated based on the selling price multiplied by the number of products successfully sold in the market. The definition of Break Even Point (BEP), according to Hansen/Mowen (2009), is the point at which total revenue equals total cost, i.e., profit reaches zero. It’s important to note that having multiple break-even points can make it more challenging for a company to achieve profitability, as it may require a higher level of sales to reach each break-even point.
The Formula and How to Calculate BEP in Investment Based on 2 Types
The contribution margin per unit is the difference between the selling price and the variable costs per unit. The break-even point is a fundamental concept that determines the level of sales or investment at which neither profit nor loss is incurred. It represents the equilibrium point where total revenue equals total costs. Whether you are running a business or engaged in financial markets, identifying the break-even point is essential for assessing the viability of your operations. Normal profit, also known as zero economic profit, is the minimum profit a business requires to keep operating in its current activity.
- It’s essential for determining the minimum sales volume required to cover total costs and break even.
- The shut-down point represents a critical threshold where a firm decides it’s better to temporarily stop production rather than continue operating.
- At this decision point, a firm can choose to either continue to operate, or to shut down temporarily.
- For the period considered, the result is zero, meaning that there is neither profit nor loss.
- Break even analysis is the technique of determining the break even point for a product taking into account several other factors.
Business and Stock Market Scenarios
Therefore, QuickBooks ProAdvisor the importance of break-even point for sound business and decision making cannot be overemphasized. To sum up, the breakeven point is a crucial concept in finance and business strategy, providing insights into financial viability and profitability. By calculating the breakeven point, businesses and investors can make informed decisions, set revenue targets, and manage risks effectively. Ultimately, breakeven analysis plays a significant role in sales assessment, enabling businesses to set realistic objectives and manage risks effectively.
- These concepts illustrate the elegant rationality underlying market behavior in perfectly competitive industries.
- The break-even point (BEP) is the level of sales at which total revenue equals total costs, resulting in zero profit or loss.
- Between these points lies the territory where firms operate at a loss but continue production because they cover variable costs and some portion of fixed costs.
- After identifying the types of production costs, it is now possible to calculate the break-even point of production because this is where you will either make a profit or a loss.
- First, let us give you a brief idea of what these numbers from General Motors’s Annual Report (or 10K) signify.
- Now you can boldly reinvest profits into innovation, research, and development, or even enhance your marketing efforts to catapult your business to the next level.
Break-even Analysis: Importance, Uses, Components and Calculation

By emphasizing research and understanding the crypto market, you can increase your chances of investment success, reduce risk, and make smarter decisions based on valid data. It reduces the risk of possible losses and simultaneously increases the overall profitability of the business. In other words, BEP helps a company in risk management and decision-making that positively impacts its profitability. The BEP function is very important in monitoring changes in the value of profits that may occur due to changes in product prices. This concept comes from the understanding that the BEP value and the price of the product sold are linear.
- For variable costs per unit, we divided the line item “Automotive and other costs of sales” with the number of units sold.
- In effect, the insights derived from performing break-even analysis enables a company’s management team to set more concrete sales goals since a specific number to target was determined.
- If you buy shares at a certain price, your break-even point is when the stock’s market price climbs back up to your purchase price after any dips.
- At this sales volume, the revenue ($8,350) exactly covers all fixed and variable costs, resulting in zero profit and zero loss.
- To do so, it will have to scale operations and make significant capital investments in factories and labor.
- The shut-down point of production, on the other hand, is the price at which the marginal cost equals average variable costs (AVC).
Uses of break-even price
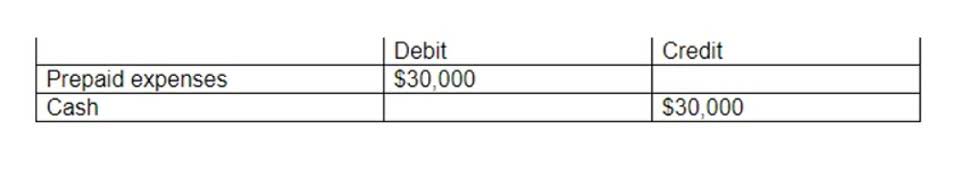
The accounting Break-even Point is calculated by taking the total expenses on a particular production and calculating how many units of the product must be sold to cover the break-even point definition economics expenses paid. The hard part of running a business is when customer sales or product demand remains the same while the price of variable costs increases, such as the price of raw materials. When that happens, the break-even point also goes up because of the additional expense. Aside from production costs, other costs that may increase include rent for a warehouse, increases in salaries for employees, or higher utility rates.

When profit exceeds normal profit, or break-even profit, it is called positive economic profit. Normal profit how is sales tax calculated is the benchmark for determining if a business has been successful. As you can see, the Barbara’s factory will have to sell at least 2,500 units in order to cover it’s fixed and variable costs.